The lender must select one of the two alternatives and apply the method consistently throughout the life of the loan. Adjust for the “missing pennies” (noted in red) Budgeting for Nonprofits and total the bond payment amount, interest at yield rate, and amortized premiums. Amortization journal entries are included in the Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR) section. CPA examinees should learn how to account for intangibles, bond premiums and discounts under US GAAP. When the amortization period of the loan is longer than the payment term, there is a loan balance left at maturity — sometimes referred to as a balloon payment. If you have a 10 year term, but the amortization is 25 years, you’ll essentially have 15 years of loan principal due at the end.
Amortizing Bond Premium With the Constant Yield Method

In this article, you will learn about how to prepare a how to calculate premium amortization bond amortization schedule in Excel. We will be using the Microsoft 365 version, however, you can follow this article using any Excel version from 2003. In this case, the bond holder essentially assumes the same role as a bank lending a 30-year mortgage to a home buyer.
Straight-Line by Maturity
- The difference between the price we sell it and the amount we have to pay back is recorded in a contra-liability account called Discount on Bonds Payable.
- It encourages students and practitioners to use the concept in real-life scenarios.
- In our example, the bond premium of $4,100 must be reduced to $0 during the bond’s 5-year life.
- An amortization schedule, often called an amortization table, spells out exactly what you’ll be paying each month for your mortgage.
- The straight-line method is a linear method that is the simplest to use.
- When they are issued at anything other than their par value a premium or discount on bonds payable account is created in the bookkeeping records of the business.
Consider software which is bought at ₹1,00,000 and has a useful life of 5 years. Straight line amortization is a method for charging the cost of an intangible asset to expense at a consistent rate over time. This method is most commonly applied to intangible assets, since these assets are not usually consumed at an accelerated rate, as can be the case with some tangible assets. In an amortization schedule, each repayment installment is divided into equal amounts and consists of both principal and interest.
- This method is most commonly applied to intangible assets, since these assets are not usually consumed at an accelerated rate, as can be the case with some tangible assets.
- This way, the issuer’s income statement reflects the true cost of financing its operations with the bond.
- Amortization schedules, bonds payable, bond calculation methods, and more.
- The premium on bonds payable account has a credit balance of 9,075 which needs to be amortized to the interest expense account over the lifetime of the bond.
- To calculate the present value of the semiannual interest payments of $4,500 each, you need to discount the interest payments by the market interest rate for a six-month period.
- When purchasing a bond at a premium, the investor is essentially paying more for its promised future cash flows than the bond’s stated value.
📆 Date: Aug 2-3, 2025🕛 Time: 8:30-11:30 AM EST📍 Venue: OnlineInstructor: Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM
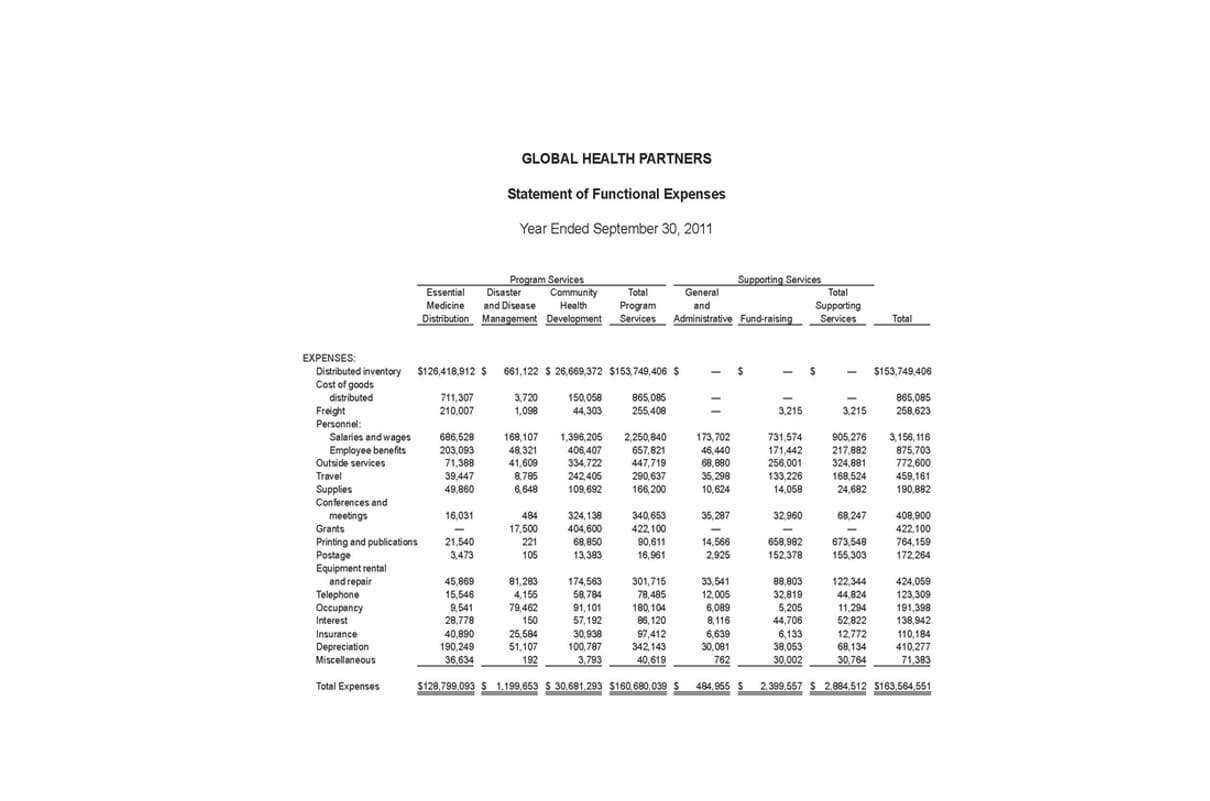
To obtain the proper factor for discounting a bond’s maturity value, use the PV of 1 table and use the same “n” and “i” that you used for discounting the semiannual interest payments. Always use the market interest rate to discount the bond’s interest payments and maturity amount to their present value. In our example, the bond discount of $3,851 results from the corporation receiving only $96,149 from investors, but having to pay the investors $100,000 on the date that the bond matures. The discount of $3,851 is treated as an additional interest expense over the life of the bonds. When the same amount of bond discount is recorded each year, it is referred to as straight-line amortization. In this example, the straight-line amortization would be $770.20 ($3,851 divided by the 5-year life of the bond).
A bond that’s trading at a premium means that its price is trading at a premium or higher than the face value of the bond. For example, a bond that was issued at a face value of $1,000 might trade at $1,050 or a $50 premium. Even though the bond has yet to reach maturity, it can trade in the secondary market.
It represents part of the cost basis for tax purposes and can be tax-deductible when using the constant yield method to spread out the deduction over the bond’s life. Amortizing bond premiums can help offset interest income, thus reducing an investor’s overall taxable income. The bond amortization aims to match the normal balance interest expense of the bond with the interest payments over the life of the bond.
AccountingTools
The bond’s price will be $1,082.64, which is the present value of its cash flows discounted at 4%. However, if the market interest rate rises to 6%, the bond is worth less than its face value, because it pays a lower coupon than the market rate. The bond’s price will drop to $923.61, which is the present value of its cash flows discounted at 6%. One big caveat about the straight-line method As simple as the straight-line method is, the main problem with it is that the IRS generally doesn’t allow you to use it anymore.

For the years in which you own the bond for all 12 months, you simply take amortization of 12 times the monthly amount. For the year of purchase and the year of sale or maturity, you have to account for a partial year, multiplying the monthly amount by the number of months during the year that you actually owned the bond. Repeat this process for each year, using the updated carrying value to calculate the interest expense, until the bond’s carrying value equals its face value at maturity. The Effective Interest Rate to Call method considers whether the stated yield is the Yield to Call or Yield to Maturity. Municipal bonds must be reported at their “yield to worst,” the lowest possible yield. In the event a bond is a callable premium bond, there is a higher likelihood that the bond will be called before or at the call date.

5 Interest method
- Understanding how bond discounts are amortized is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance.
- The straight line method amortization for each period, and produces an effective interest method amortization schedule showing the premium or discount to be amortized each period.
- The IRS’s preferred approach for calculating bond premium amortization involves using the Constant Yield Method (CYP).
- This, in turn, will reduce the amount of taxable income the bond generates, and thus any income tax due on it as well.
- We will also look at some of the different perspectives of bond investors, issuers, and accountants regarding interest rates and bond value.
The calculation will result in a sequence of negative values representing the annual amortizable bond premium expense. Suppose, for example, a business issued 10% 2-year bonds payable with a par value of 250,000 and semi-annual payments, in return for cash of 241,337 representing a market rate of 12%. Suppose, for example, a business issued 10% 2-year bonds payable with a par value of 250,000 and semi-annual payments, in return for cash of 259,075 representing a market rate of 8%. Bond amortization can be used to measure the performance and risk of the bond investment.
Leave a Reply